FE model for Intermediate crack induced debonding in RC beams strengthened with FRP plates
|
A
finite element model for intermediate crack induced debonding (IC
debonding) in RC beams strengthened with FRP plates is proposed,
which is based on smeared crack model for concrete. Comparing with
test results, this model can precisely predict the debonding behavior
of IC debonding.
Supervisors: Prof. J. G. Teng of the Hong Kong Polytechnic University. Prof. L. P. Ye and J. J. Jiang of Tsinghua University Paper download Intermediate
crack debonding in FRP-strengthened RC beams: FE analysis and
strength model Abstract: Reinforced concrete (RC) beams strengthened in flexure with a bonded fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) plate may fail by intermediate crack (IC) debonding, in which debonding initiates at a critical section in the high moment region and propagates to a plate end. This paper first presents a finite-element (FE) model based on the smeared crack approach for concrete for the numerical simulation of the IC debonding process. This finite-element model includes two novel features: (1) the interfacial behavior within the major flexural crack zone is differentiated from that outside this zone and (2) the effect of local slip concentrations near a flexural crack is captured using a dual local debonding criterion. The FE model is shown to be accurate through comparisons with the results of 42 beam tests. The paper also presents an accurate and simple strength model based on interfacial shear stress distributions from finite-element analyses. The new strength model is shown to be accurate through comparisons with the test results of 77 beams, including the 42 beams used in verifying the FE model, and is suitable for direct use in design. Finite Element Analysis of Intermediate Crack-Induced Debonding in FRP Strengthened RC Beams Engineering Mechanics (Accepted) Abstract£ºA finite element (FE) model to simulate the intermediate crack (IC) debonding of RC beams flexually strengthened with externally bonded FRP plates is presented in this paper. A dual debonding criterion is proposed so that IC debonding can be predicted with the common smeared crack approach for concrete. Furthermore, based on meso-scale FE results, proper bond-slip models for the interface between FRP and concrete are proposed. This FE model is implemented with MSC.MARC which is a widely used FE package. Through comparisons with the test results of 45 beams, this method is shown to provide accurate predictions of IC debonding failures. Key words£ºRC beam, FRP, debonding, intermediate crack, finite element analysis Recent research on intermediate crack Debonding in FRP-strengthened RC beams ABSTRACT: An important failure mode for an RC beam strengthened with an externally bonded FRP plate is debonding of the FRP plate from the soffit of the beam due to major flexural cracks. In this failure mode which is commonly referred to as intermediate crack (IC) debonding, debonding initiates at a critical section in the high moment region and then propagates to one of the plate ends. Despite many experimental and theoretical studies, accurate predictive models for IC debonding failures have not been developed. This paper presents a new smeared crack approach for the finite element simulation of the IC debonding process, in which a new model for the FRP-to-concrete interface capable of capturing the effect of local slip concentration near a flexural crack is proposed. The finite element model is shown to be accurate through comparisons with the results of 45 beam tests. The paper also presents an accurate and simple design model based on interfacial shear stress distributions from finite element analysis. The new design model is shown to be accurate through comparisons with the test results of 73 beams, including the 45 beams used in verifying the FE model.
|
|
|
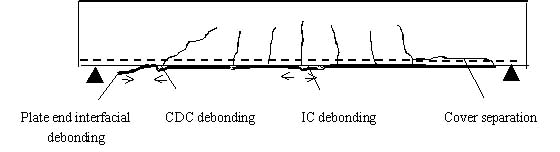
Debonding modes for RC beams strengthened with FRP plates |
|
 |
 |
|
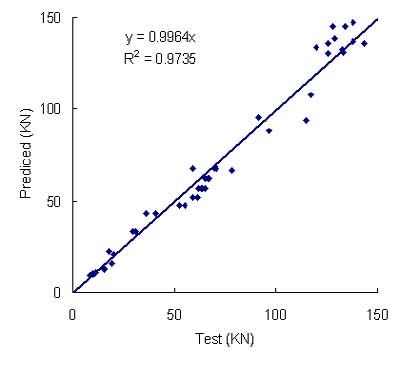
Comparison
for ultimate strength
|
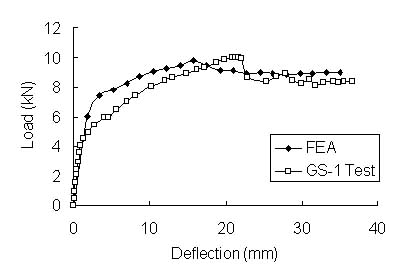
Comparison
for load-deflection curves
|
 |
|
|
Comparison
for crack patterns
|
|