某特深基坑模拟开挖有限元分析及反分析
论文下载
岩石力学与工程学报,Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,23(11), 2004,1906~1911
摘要 润扬长江大桥北锚特深基坑设计尺寸达到69×50×50m,支护方案为嵌岩地连墙加内支撑结构形式。为了深入了解该基坑支护方案的安全储备情况,并预测其可能的破坏形式,在模拟施工过程的三维非线性有限元分析的基础上,通过人为加大土体自重直至支护结构破坏的方法,对该基坑进行了破坏模拟分析。分析结果说明,该基坑的破坏都始于支撑的压坏,进而使地连墙屈服或折断。而在不同开挖深度下,基坑的破坏形式有所不同。开挖深度越深,破坏造成的危害也越大。
关键词 深基坑,三维有限元分析,破坏模式;
Abstract: The size of the north anchor deep pit of Runyang Bridge is about 69×50×50m. The excavation support structure in this pit is concrete diaphragm wall with internal support structure, and the diaphragm wall is embedded into rocks. In order to know the safety margin and the failure process of this pit, 3-D nonlinear finite element analysis with excavation simulation is carried out with the finite element analysis software of ANSYS. The excavation process is simulated with the “Element Die/Active” function of ANSYS. The self-weight of soil in the finite element model is increased hypothetically until the support structure is destroyed, so that the failure process of support structures can be simulated. Comparing the assumed self-weight of soil to the real one, the safety margin of the pit can be obtained. The numerical results show that all the failures of the pit begin with the collapse of the internal support and the failure models are different in various excavation depths. This method also can be applied to other pits if their support structure is relatively stiff.
Keywords: deep pit, spatial finite element analysis, failure model.
岩土工程学报,Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,25(4), 2003,488~491
摘要:某特深基坑设计尺寸达到69×50×50m,且施工场地地质条件较差,基坑变形控制严格,用普通近似方法分析和设计有较大的难度。为了准确了解基坑支护结构的内力和变形情况,确保工程安全,本文对该基坑进行了施工全过程的三维有限元弹塑性分析和模拟,并详细说明了其具体实现方法。有限元分析中分别考虑了支护结构和土体之间的相互作用问题,以及各种开挖方案、降水方案对基坑变形的影响,并对各种关键参数进行了参数敏感性分析和讨论。对比各种分析结果,考虑共同作用和不考虑共同作用基坑变形相差达到10倍,支护结构内力相差达到1.5倍。同时,不同开挖方案及降水方案对变形和内力也有着重要影响,各方案之间最终差别甚至可以达到1倍以上。分析结果说明,对于这类复杂工程,进行考虑结构与土体共同作用的施工全过程三维有限元分析和模拟是完全必要和必须的。
关键词:共同作用,基坑工程,三维有限元分析
Abstract: The size of a very deep pit is about 69×50×50m and it is difficult to analyze with traditional approximate method. In order to know the details of the deformation and internal force of the excavation support structure, spatial non-linear finite element analysis is carried out in which the excavation process is considered. The interaction between the excavation support and the soil, the difference between various excavation plans, the influence of ground water lowering and sensitive analysis of critical parameters are discussed in detail. The numerical results show that the deformation of the continuous concrete wall with interaction effect will be 10 times of that without interaction effect, while the difference of support axial force will be 1.5 times in the two cases. At the same time, the excavation plan and ground water lowering are also important for the deformation and internal force in the support. The analysis results show that the interaction between soil and structure and simulation of excavation process are necessary in such complex problems.
Keywords: interaction, deep pit, spatial finite element analysis
基坑开挖全过程分析
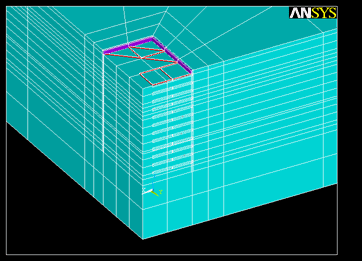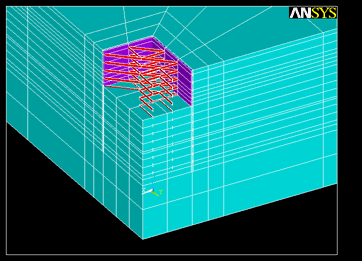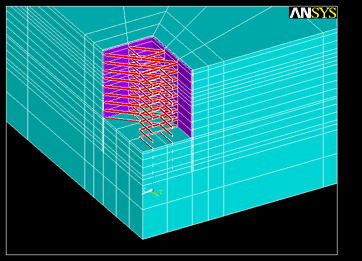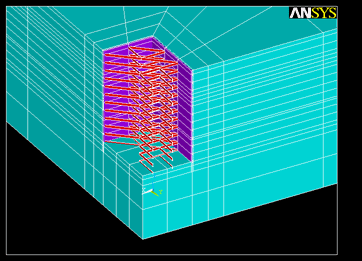
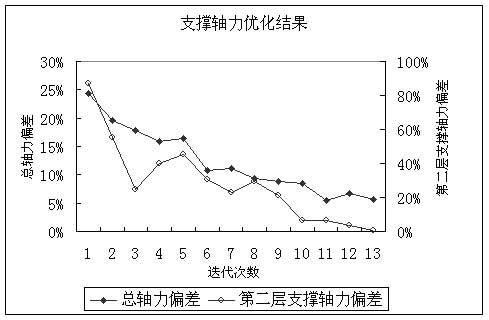
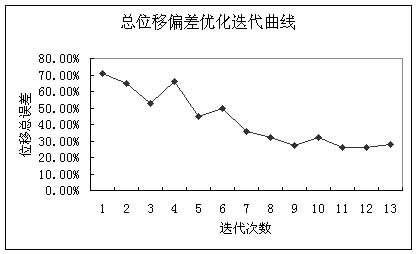
反演分析迭代过程
|
 |