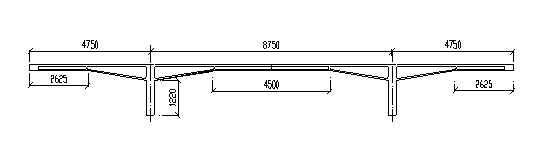
Experiment and Analysis for A Large-scale Bridge Model
A large-scale PC continuous rigid frame bridge model
with a total length of 18m is tested and its deformation, strength and
long-term performance are analyzed and damage detection is studied during
the test.
Paper download
Prediction
of bridge bearing capacity based on high-precision nonlinear finite
element analysis and fast modeling technology,
Journal of Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2009, 28(4):
12-16.
Abstract: Fast and accurate prediction
for the bearing capacity of bridges after inspection is important for
the management and retrofitting of bridges. This paper presents the
study on the bearing capacity of bridges based nonlinear finite element
analysis. The accuracy of the proposed high-precision nonlinear finite
element model is verified via a large scale bridge model experiment.
And a fast modeling technology is development to reduce the workload
of high-precision modeling. Finally the application of the proposed
technology is demonstrated with real projects.
Keywords: bridge, prediction of bearing capacity, nonlinear finite
element, high-precision, fast modeling
Experimental
study on prestressed-high-strength-light-weight-concrete continuous
rigid frame bridge
Engineering Mechanics, 24(sup.I), 2007, 134-140.
Abstract£ºHigh strength light weight
concrete (HSLWC) (with a cube strength higher than CL40) has a bright
future in the application of large-span bridges for its obvious advantages.
It can reduce the self-weight of the bridge, so that the internal stress
will be smaller, the span will be larger and the number of piers will
be reduced. An experimental research on a 3 span prestressed continuous
rigid frame model bridge with a superstructure made up with CL50 HSLWC
is presented in this paper. The archetype of the bridge model is located
in the 14th construction section of the highway connects Anning and
Chuxiong in Yunnan province. The model bridge was designed by the scale
of 1/4 and was tested under 10 different load cases. The test results
showed that the prestressed HSLWC continuous rigid frame model bridge
had good mechanical performance. Under a traffic load which was 1.0
to 1.5 times to its design load, all indices of the bridge model can
satisfy the requirement of design standard. And under 2 times of design
load, parts of indices were beyond the standard requirement but the
bridge still showed good ductility. And under very large overload situation,
the bridge was damaged seriously but it still can maintain the load
capacity and would not collapse.
Key words£ºrigid frame bridge£»model experiment£»high strength lightweight
concrete£»prestress£» residual deformation
Nonlinear
finite element analysis for a prestressed continuous rigid frame concrete
bridge
Proc. International Symposium on Computational Mechanics
(ISCM2007), Yao ZH & Yuan MW (eds.), Beijing: Tsinghua University
Press & Springer, July 30-August 1, 2007, Beijing, China, 267 &
CDROM.
Abstract: Bridges in China are always
suffered from the overload traffic. So precise assessment for the safety
of the bridges is important. Nonlinear FE analysis with the consideration
of damage accumulation, material nonlinearity and boundary connection
is a powerful tool for this problem, which is cheaper than test and
more accurate than linear FE analysis. But nonlinear FE analysis for
prestressed concrete bridge in China still has not been widely accepted.
Hence, in this paper, a nonlinear FE analysis for a prestressed continuous
rigid frame concrete bridge is implemented with the comparison of a
large-scale bridge experiment so as to discuss the modeling technique
and to verify the result of numerical model. Nonlinear behaviors such
as prestress, cracks, crush of concrete, yield of rebar and contact
of support are taken into account. Ten different load cases to represent
different overloads are all simulated in both FE model and experimental
model. Through the analysis, it can be concluded that nonlinear FE model
correctly monitor the performance and damage of the bridge.
Key words: bridge, nonlinear analysis, FEA
Large-scale
experimental study on the safety monitoring for continuous rigid frame
concrete bridges
Proc. 2006 International Symposium on Safety Science
and Technology (2006 ISSST), Science Press, Changsha, China, 2278-2283
Abstract: During the service life
of a bridge, it is impossible to avoid damage accumulation and function
degeneration due to traffic load, environmental corrosion and accidental
punch. Hence, the safety monitoring of bridges have been received wide
focus to prevent the sudden fatal accidents. This paper presents a large-scale
experimental study on the safety monitoring for continuous rigid frame
concrete bridges, which has 3 spans and a total length of 18m. Ten different
load steps were tested to simulate different levels of overload, and
curvature mode method was adopted to detect the damage after the load
cases. By monitoring the changes of curvature modes, the damage detection
shows good performance to give the safety situation and the damage position
of the bridge. So it can be concluded that this method could be used
in real structures to guarantee the safety service of the bridges.
Key words: bridge; safety monitoring; damage detection; curvature
mode
Experimental
research and damage assessment for a large-scale PC continuous rigid
frame bridge model
Proc. 17th National Conference of Bridges. Chongqin,
China, 2006. 907-913.
Long Term Deformation
Analysis of Shrinkage and Creep of Steel-Concrete Composite beams
Building Structure, 36(sup), 2006: 9-8~11.
Abstract: Based on the theory of fiber model, an efficient numerical method to account for the long-term behavior of composite steel-concrete beams is presented, the creep and shrinkage value is proposed by MC90 model. Numerical results are compared with the experimental results and a good agreement reached. It is found that the design methods for the long-term deflection of current Chinese codes are unsafe while other proposed methods have some drawbacks. A simplified approach to evaluate creep and shrinkage effects in simply supported composite beams is presented. The deflection induced by creep is based on effective modulus method and the deflection induced by shrinkage is directly computed. With clear physical concept, the method is more reliable and in good agreement with the test results.
Keywords: Steel-concrete Composite
Beam; Shrinkage; Creep; Fiber Model; Long-term Deformation; Effective
Modulus